Introduction
This reference is about API version 3. If you are using old sites you cannot use this API to have access to the devices on this sites.
See our 3.0 overview to learn new features.
API Design
The Enapter HTTP API is a resource-oriented API in which each node is either a single resource or a collection of resources. Interaction with resources occurs through a set of standard and additional methods. Standard methods are a set of CRUD operations. Additional methods are used to express operations that cannot be performed using standard methods.
Enapter API resources
- Blueprints
- Sites
- Devices
- Device Commands
- Device Properties
- Device Logs
- Device Telemetry
- Rules
- Telemetry
Standard Operations
Create— creates a new resource and returns created resource representation.Get— returns resource representation by identifier. Resource can be expanded with additional fields. See Get Device for example.List— returns list of resource representations. Each resource in the list can be expanded with additional fields. See List Devices for example.Update— updates a resource and returns updated resource representation.Delete— removes a resouce.
API Base URL
Use the following base URLs to access this API:
- Enapter Cloud:
https://api.enapter.com - Enapter Gateway:
http://enapter-gateway.local/api
When your devices are connected to the Enapter Cloud — even through the Enapter Gateway — you can remotely monitor and control them from anywhere in the world with an Internet connection.
For the offline Enapter Gateway, you must be on the same local network to enable remote control and monitoring.
Authentication
Enapter HTTP API uses API tokens to authenticate requests. Without token request will be authenticate as from anonymous user. Some API endpoints can work without authentication. For example your can validate or download blueprint without token.
The token should be provided via custom HTTP header X-Enapter-Auth-Token:
$ curl https://api.enapter.com/v3/devices -X GET \
-H 'X-Enapter-Auth-Token: {ACCESS_TOKEN}'
$ curl http://enapter-gateway.local/api/v3/devices -X GET \
-H 'X-Enapter-Auth-Token: {ACCESS_TOKEN}'
API token
Before getting started, you need to get credentials. Enapter API requires access token for authentication.
Cloud
You must have the Enapter Cloud account.
- Go to Enapter Cloud.
- Click on Account Settings in the upper right corner.
- In API Tokens click on New Token
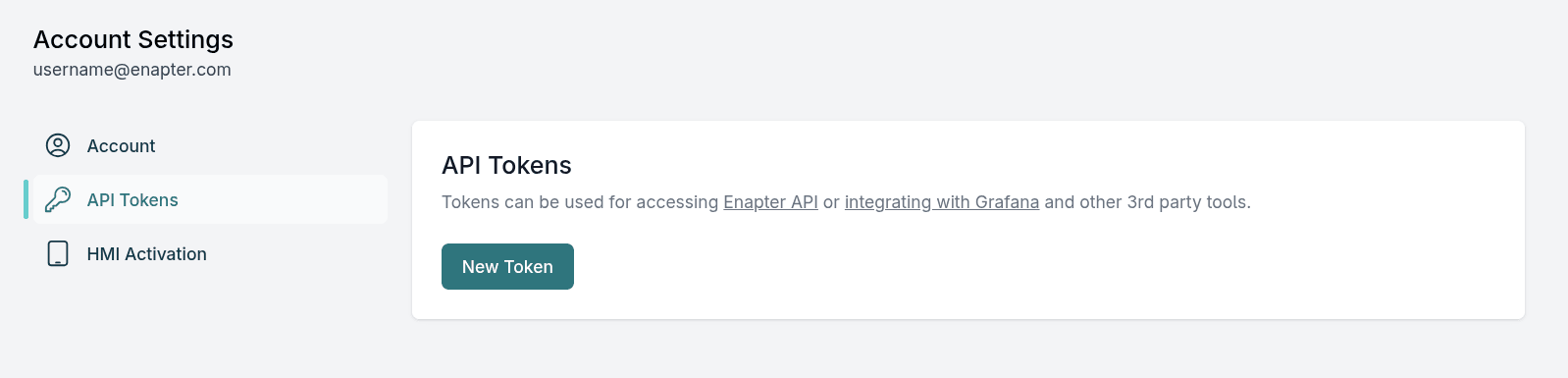
- Type in an informative token name and click Create Token
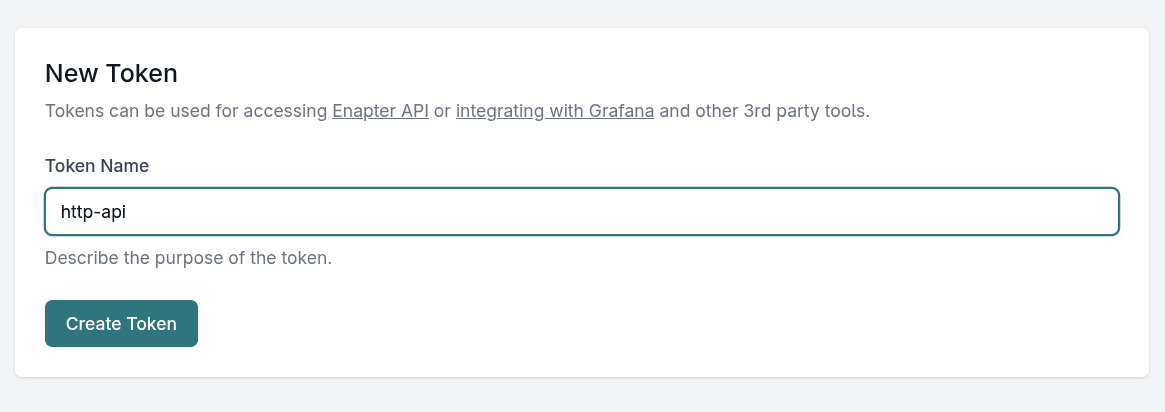
- Copy your token and save it somewhere (e.g. your password manager) to use it with API calls.
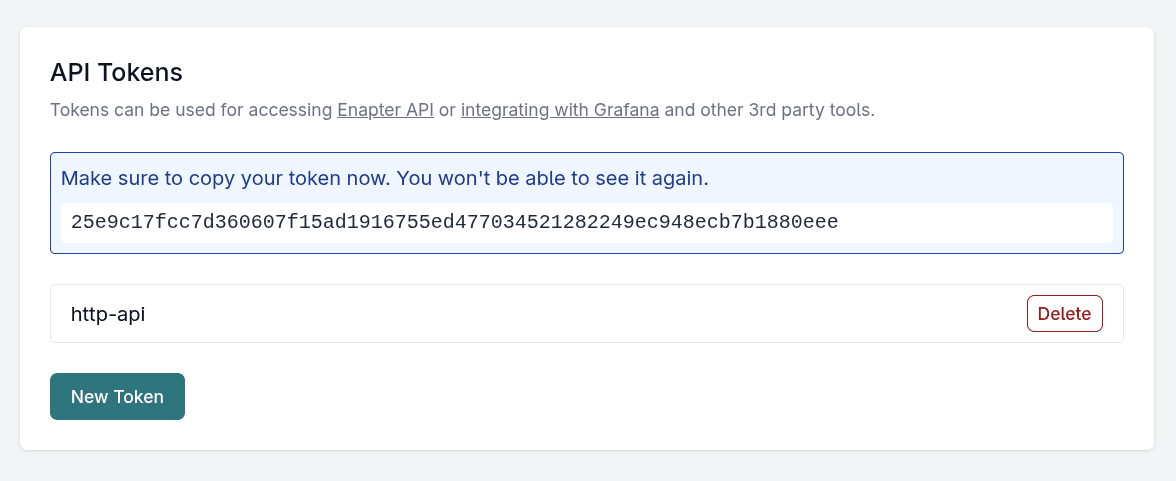
Gateway
- Set your Gateway up.
- Use your Gateway IP address as a server base address and
/apias a URL subdirectory. For example, if192.168.10.22is Gateway IPv4 address, all API URLs should start withhttps://192.168.10.22/api. If mDNS resolution works well,https://enapter-gateway.local/apiwill also work as an API address. - Go to System Settings -> API Token.

- Copy your token and save it somewhere (e.g. your password manager) to use it with API calls.
Usage
$ curl http://api.enapter.com/v3/sites/fecbbba0-79f2-4e9e-a6f0-69a310ab110b \
-H 'X-Enapter-Auth-Token: 25e9c17fcc7d360607f15ad1916755ed477034521282249ec948ecb7b1880eee'
Authorization
The table below shows the access roles and their corresponding permissions.
| Actions / Roles | READ_ONLY,USER | OWNER,INSTALLER,VENDOR |
|---|---|---|
| Get device/site info | ✅ | ✅ |
| Update device/site | ❌ | ✅ |
| Delete device/site | ❌ | ✅ |
| Provisioning | ❌ | ✅ |
| Change blueprint | ❌ | ✅ |
Upon creating a site, you will automatically gain INSTALLER access to all devices that will be connected to it.
Access to different part of device are configured via blueprint by blueprint authors. The minimal required role can be set in manifest for properties, telemetry, commands, and configuration groups.
Errors
Enapter uses conventional HTTP response codes to indicate success or failure of an API request. Codes in the 2xx range indicate success. Codes in the 4xx range indicate request payload errors. Codes in the 5xx range indicate Enapter servers' errors.
| HTTP Status Code | Explanation |
|---|---|
| 200 — OK | Everything worked as expected. |
| 400 — Bad Request | The request payload has failed parsing or validation. |
| 401 — Unauthorized | Authentication token is missed. |
| 403 — Forbidden | Authentication token is invalid or expired. |
| 404 — Not Found | A non-existent resource is requested. |
| 409 — Conflict | Entity already exists. |
| 422 — Unprocessable Entity | Unable to process the contained instructions. |
| 429 — Too Many Requests | Too many requests hit the API too quickly. |
| 500 — Internal Server Error | Something went wrong on Enapter's end. |
Error Response
Any error response contains at least one error in the body.
{
"errors: [
...
]
}
Error Object
Each error has a common format.
codestringrequired#A short string indicating the reported error code.
messagestringrequired#A human-readable message that provides more details about the error.
detailsobject#Additional error-specific fields.
{
"code": "invalid_header",
"message": "Authentication token is invalid.",
"details": {
"header": "X-Enapter-Auth-Token"
}
}